TAB Reader 4 and TAB Reader 5 - What has changed?
New user interface
All TAB Reader tools have been reworked including new user interface and broader possibilities for data processing. Some new options and interface elements are presented below.
Input files/data selection
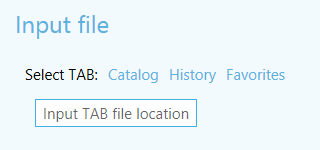
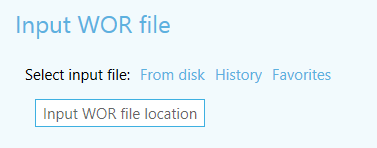
Figure 1 Selection of input data interface elements
New version has new additional selection methods for input files/data, which allow to significantly save operation flow time:
- Map content
Selection of input data from current map. - Catalog
Selection of input data from ArcGIS Catalog application. - History
Selection of input dataset from previously used sets. This option is available if there is at least one saved dataset. - Favorites
Selection of input dataset from favorites list. This option is available if there is at least one dataset added to favorites list.
Setting output data
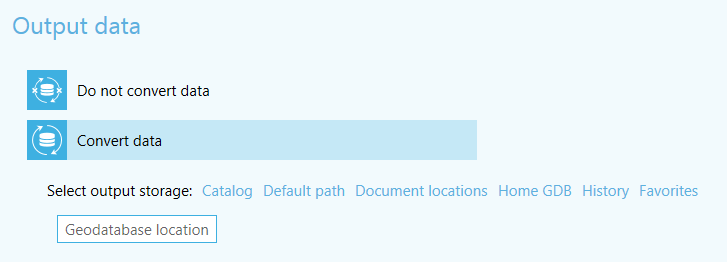

Figure 2 Setting output data interface elements
Possibilities to set output data were also enhanced which has significantly sped up the process of tools setting up procedures.
Methods of setting output data:
- Catalog
Setting the name of output geodatabase and its location in ArcGIS catalog. - On disk drive
Setting the path to output map/layer on disk drive. - Default path
Recovery of the default path set for output data. - Home folder
Saving of output dataset in geodata home folder. - History
Selection of location for output dataset from previously used folders. - Favorites
Folder selection for storing the output map document mxd, lyr file and other results of conversion from favorites list. This option is available if there is at least one geodatabase or folder added to favorites list.
Creation of names
New version has an option to create complex names for conversion objects. This can be done using standard Expression dialog window, opened via “Edit…” button.
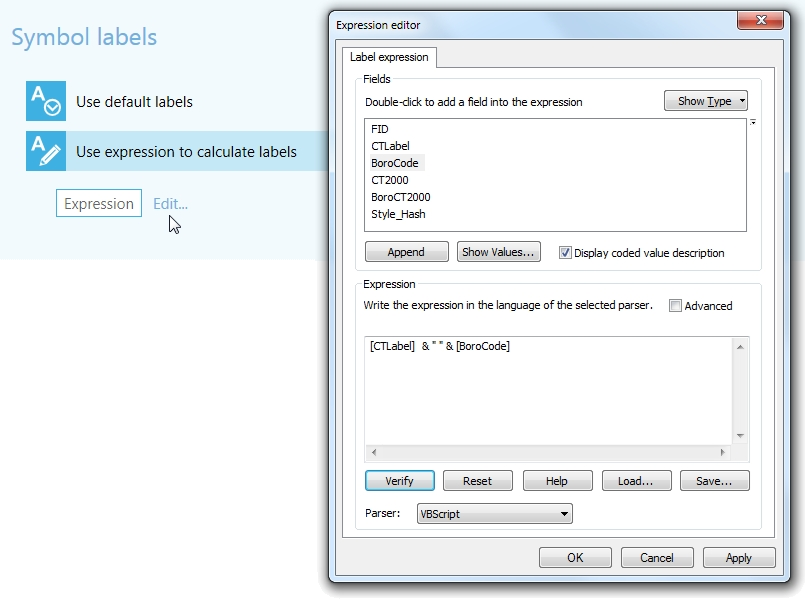
Figure 3 Symbology labeling parameters
History
New tools allow to create and work with history lists. Using history makes it quicker and easier to select input and output data. Besides, history can be used to see recently used datasets.
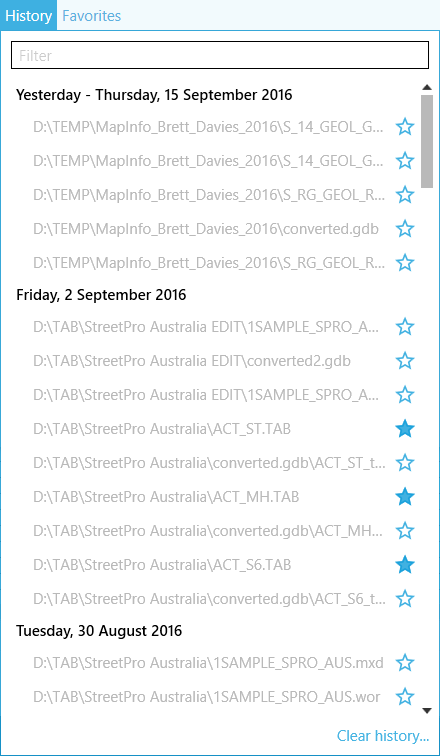
Figure 4 History list
Favorites
Favorites list can be created and managed in new TAB Reader version. Favorites is a manually managed list of selected datasets. By checking/unchecking star icon of the required element of the list, it can be added/removed from the favorites list. As a result, it is much quicker and more convenient to search for desired data.
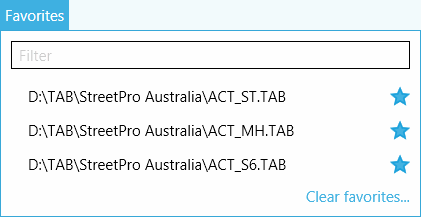
Figure 5 Favorites list
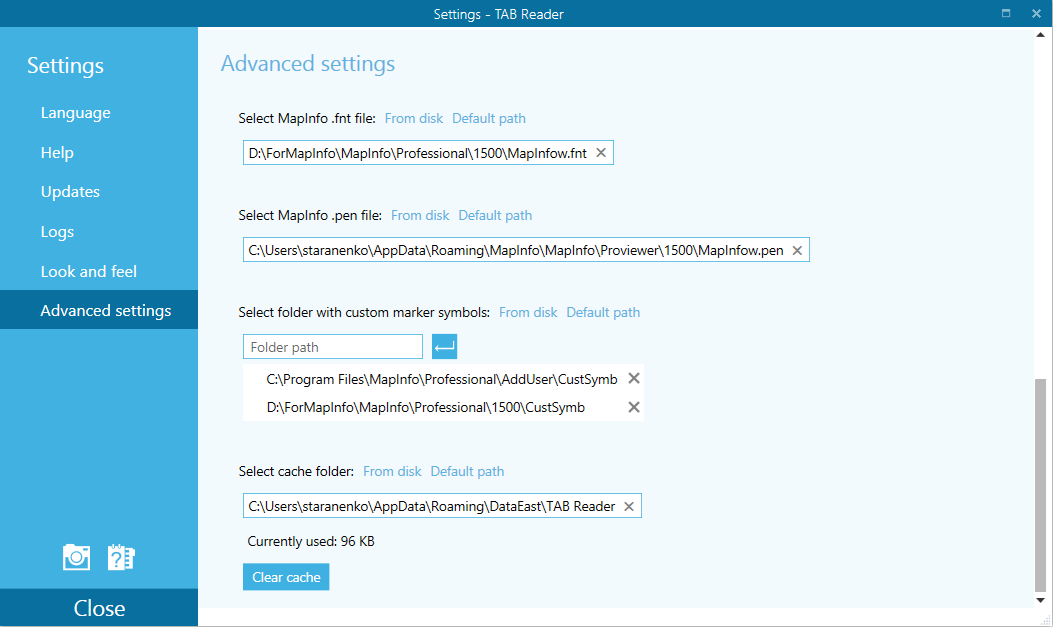
Symbols and line styles library
New version has support for standard and custom MapInfo styles and symbols (MapInfow.pen, MapInfow.fnt, FillSymbols). Now it is possible to set required style library and obtain the corresponding map appearance.
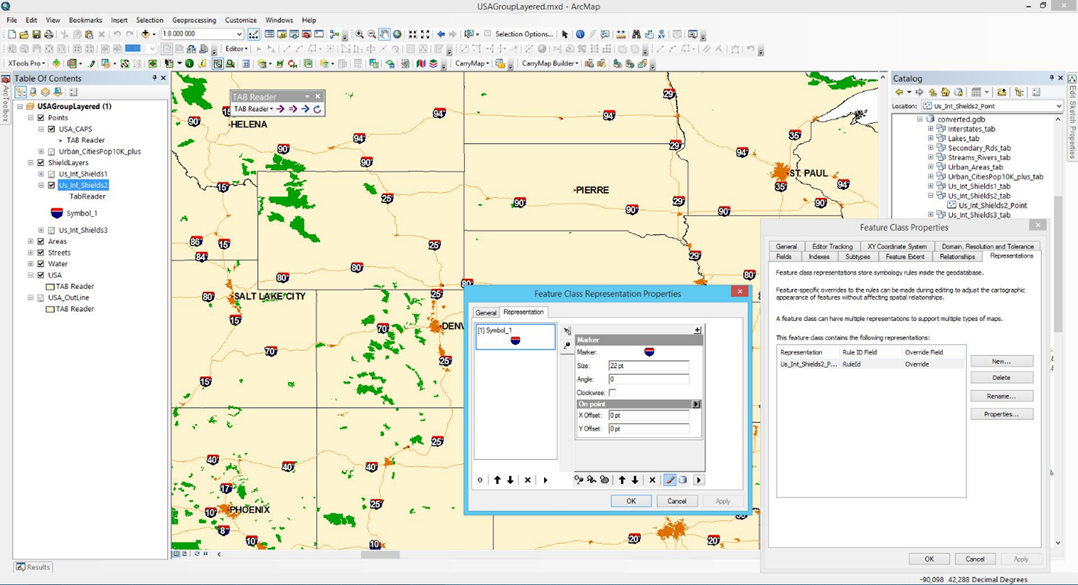
Representations
MapInfo symbols can be saved as representations of ArcGIS feature classes in geodatabase, map document or LYR file. This option can be useful for their editing and subsequent use with current, as well as new data, and also for exchange of symbol sets between users.
Other useful features
New additional tools allow to automate work with the help of Python scenarios generation, as well as take screenshot of tool parameters screen:
- Work with Python: get Python script with possibility to save it to file or clipboard.
- Possibility to save tool dialog with set parameters by saving screenshot to clipboard or file which can be later sent to developer team with the description of the occurred problems.
- Help Topics.
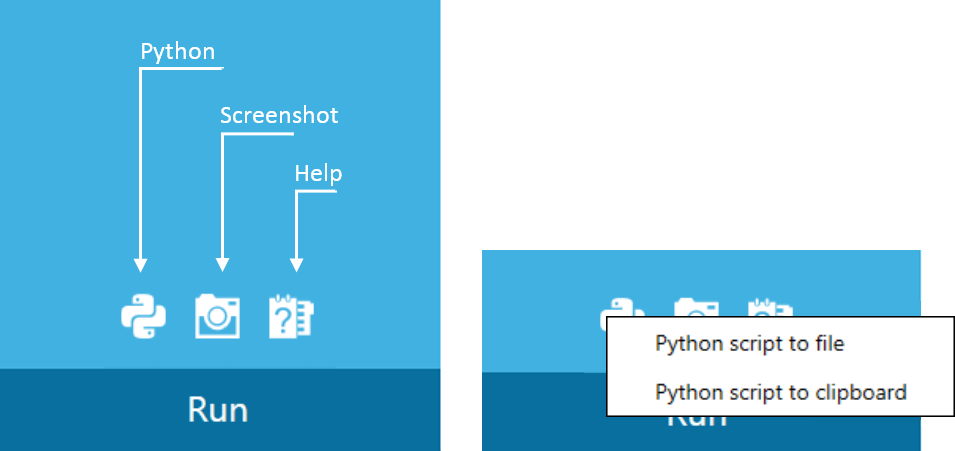
Figure 6 Additional features
Geoprocessing tools
New tools are implemented as geoprocessing tools which combine benefits and usability of modern interface and all advantages of geoprocessing environment, including 64-bit background geoprocessing environment, use of Python in scripts and models.
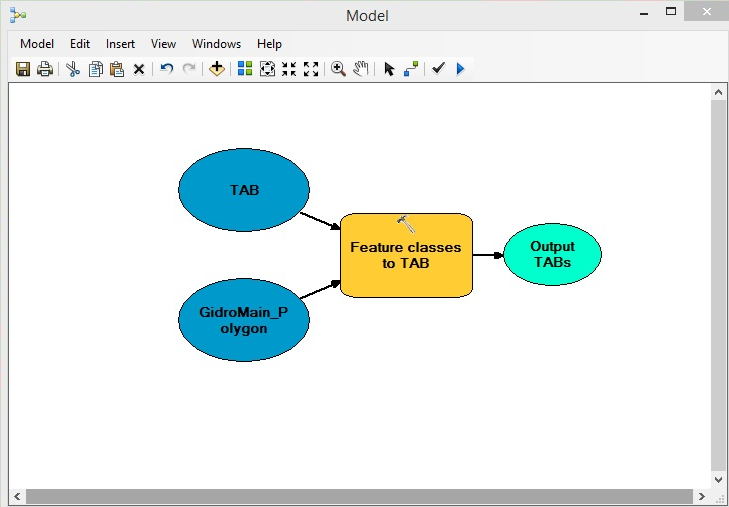
Figure 7 Example of using tools in models
TAB Reader geoprocessing tools are tightly integrated with ArcGIS geoprocessing parameters. In particular, the following parameters are taken from ArcGIS geoprocessing parameters:
- Overwriting geoprocessing operations results
- Adding geoprocessing operations result to map
- Enabling background processing.
The TAB Reader geoprocessing tool list provides high work automation level for the following processes:
- TAB to ArcGIS
- TAB to ArcGIS (batch processing)
- WOR to ArcGIS
- Feature classes to TAB.